fr
noms dans le fil d’Ariane


La lletxa o lliri (Campogramma glaycos) és un peix teleosti de la família dels caràngids i de l'ordre dels perciformes.[2][3]
Campogramma glaycos és l'única espècie del gènere Campogramma.[4]
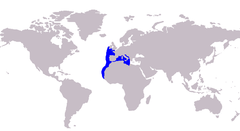
Es troba a les costes de l'Atlàntic oriental (des de les Illes Britàniques fins al Senegal, incloent-hi l'Arxipèlag de Madeira i les Illes Canàries).[6] Penetra a les costes de la Mar Mediterrània a la primavera.[7]
La lletxa o lliri (Campogramma glaycos) és un peix teleosti de la família dels caràngids i de l'ordre dels perciformes.
The vadigo, Campogramma glaycos (also known as the big-toothed pompano, zippered pompano, lexa and lexola), is a species of medium-sized coastal marine fish in the jack family, Carangidae. The species is distributed throughout the eastern Atlantic Ocean from the British Isles in the north to Senegal in the south, also entering the western Mediterranean Sea. The vadigo is similar in form to both the leatherjacks and the queenfish, but can be distinguished by its scaleless chest and a broad, rounded upper jaw. It is a predatory fish, preying mostly on smaller schooling fishes. The species was initially classified under the genus Centronotus before being transferred to its own monotypic genus of Campogramma. The vadigo is of minor commercial importance throughout its range, and is also considered to be a game fish.
The vadigo is the only species classified in the monotypic genus Campogramma, which itself is one of 31 genera in the family Carangidae, which contains the jacks, horse mackerels and pompanos. The Carangidae were classified as Perciform fishes in the suborder Percoidei,[3] but most authorities now classify the carangids in the order Carangiformes along with the remoras, dolphinfishes and related families.[4]
The species was first scientifically described by Bernard Germain de Lacépède in 1801 under the name of Centronotus glaycos.[2] In 1903, Charles Tate Regan transferred the species to a new genus, Campogramma, creating the valid combination in use today (Centronotus is now considered a synonym of Naucrates). The species has two junior synonyms, the first was described in 1941 as Oligoplites africana by Delsman and the second in 1955 by Dollfus, who named Campogramma lirio.[2] Early phylogenetic treatments of the species placed it in the subfamily Trachinotinae without substantiating evidence.[5] A review of the genus by Smith-Vaniz and Staiger cited several anatomical characters which were incompatible with the Trachinotinae, however would group it within the Naucratinae.[5] They further suggested it was a close relative of Seriola, which was later reaffirmed by a comprehensive overview of the carangids by Gushiken. In this study, it was found to be most closely related to the rainbow runner, Elegatis bipinnulata, with both Campogramma and Elegatis basal members of Naucratinae.[6] No recent genetic studies have investigated the species.
The species is commonly known as the vadigo, which is the designated FishBase name, as well as the big-toothed pompano, zippered pompano, lexa and lexola.[7]
The vadigo is similar in form to other carangids, particularly the genera Oligoplites and Scomberoides, commonly known as queenfish and leatherjacks. It is a moderately large fish growing to 60 cm (24 in), although some less reliable sources state a maximum length of 65 cm (26 in). The maximum published weight of 2.8 kg (6.2 lb). It has an elongate, moderately deep and slightly compressed body, with the dorsal profile slightly more convex than the ventral profile.[8] The upper jaw is broad and rounded at its end with a single row of large, widely spaced canines in both the upper and lower jaw. The dorsal fin is in two parts; the first consisting of 6 or 7 short, often unconnected spines while the second dorsal fin consists of a single spine followed by 26 to 28 sof rays.[9] The anal fin is similar in appearance to the second dorsal fin, having two detached spines followed by one spine attached to 23 to 25 soft rays. Both the ventral and pectoral fins are short, with the ventral consisting of one spine followed by 5 soft rays and the pectoral having 17 rays. The caudal fin is large and highly forked having 30 rays in total.[9] The body is covered in small ctenoid scales except for part of the chest area which is naked. The species has no scutes. The vadigo has 24 vertebrae in total, and has 4 to 6 upper gill rakers and 9 to 12 lower rakers.[8]
The vadigo has a steel blue to green upper body extending to midway down its side where the darker colour terminates in a series of zig-zagging lobes, with the ventral colour being silver to white.[8] All fins are hyaline to grey with the exception of the caudal fin which is often yellowish.
The vadigo inhabits the eastern Atlantic Ocean only, distributed from The British Isles in the north to Senegal in the south, with the species also found around distant offshore islands including Madeira and the Canary Islands.[2] The species is also common in the western Mediterranean Sea, where it has recently been found to extend as far north as the Adriatic Sea. The authors who reported this northern capture believe this shows an expansion of the vadigo's range, comparing it to a number of other carangid species who have recently been found outside of their normal range.[9]
The adults of the species are pelagic or epibenthic, inhabiting mostly shallow waters between 15 and 30 m in depth.[8] It moves to more coastal waters during the summer in the Mediterranean.[10]
The vadigo is a predatory fish, which takes smaller species of schooling fish as its primary prey.[8] Little is known of its reproduction and growth, with only a single juvenile described in scientific literature. The eggs of the species are known to be pelagic and occur in a single seasonal peak each year, suggesting the species has a single spawning event annually.[2]
The species is of minor importance to commercial fisheries throughout its range, often taken by bottom and pelagic trawls. It is typically sold fresh, frozen or dried and salted and is also used for production of fishmeal and oil.[8] It is considered to be a good table fish.[11] Vadigo are occasionally caught by recreational fishermen, and are considered to be a fine sports fish. They may be caught on fish baits or lures, and are most abundant in the Mediterranean between July and September.[10]
The vadigo, Campogramma glaycos (also known as the big-toothed pompano, zippered pompano, lexa and lexola), is a species of medium-sized coastal marine fish in the jack family, Carangidae. The species is distributed throughout the eastern Atlantic Ocean from the British Isles in the north to Senegal in the south, also entering the western Mediterranean Sea. The vadigo is similar in form to both the leatherjacks and the queenfish, but can be distinguished by its scaleless chest and a broad, rounded upper jaw. It is a predatory fish, preying mostly on smaller schooling fishes. The species was initially classified under the genus Centronotus before being transferred to its own monotypic genus of Campogramma. The vadigo is of minor commercial importance throughout its range, and is also considered to be a game fish.
El lichia vadigo o pez lirio es la especie Campogramma glaycos, es una especie de peces marinos de la familia Carangidae, en el orden de los Perciformes.
• Los machos pueden llegar alcanzar los 60 cm de longitud total y los 2800 g de peso.[1]
Los huevos son pelágicos.
Se encuentra en las costas del Atlántico oriental (desde las Islas Británicas hasta el Senegal, incluyendo el Archipiélago de Madeira y las Islas Canarias ).
El lichia vadigo o pez lirio es la especie Campogramma glaycos, es una especie de peces marinos de la familia Carangidae, en el orden de los Perciformes.
Campogramma glaycos Campogramma generoko animalia da. Arrainen barruko Carangidae familian sailkatzen da.
Espezie hau Egeo itsasoan aurki daiteke.
Campogramma glaycos Campogramma generoko animalia da. Arrainen barruko Carangidae familian sailkatzen da.
La leccia[1] (Campogramma glaycos), conosciuta anche come leccia fasciata o leccia stella, è un pesce d'acqua salata appartenente alla famiglia Carangidae.
Questa specie è diffusa nell'intero mar Mediterraneo e nell'Oceano Atlantico orientale tra La Manica ed il Senegal. Nelle acque italiane è molto meno comune delle altre lecce. Vive nello stesso habitat di leccia e leccia stella.
È molto simile alla leccia ma ha bocca in proporzione più piccola. Quello che la rende inconfondibile è la livrea con il dorso verdastro ed il verde madreperlaceo; il limite tra queste due colorazioni non è sfumato come nella generalità dei pesci ma è netto e segue una linea stranamente sinuosa, quasi a zig-zag. Inoltre è presente una macchia grigiastra ovoidale attorno all'occhio che gli dà un'aria stranamente "arrabbiata".
Raggiunge una lunghezza massima di 60 cm.
C. glaycos si nutre solo di pesci.
Si cattura con le stesse tecniche utilizzate per le altre lecce. Le carni sono simili, quindi ottime.
La leccia (Campogramma glaycos), conosciuta anche come leccia fasciata o leccia stella, è un pesce d'acqua salata appartenente alla famiglia Carangidae.
Campogramma glaycos is een straalvinnige vissensoort uit de familie van horsmakrelen (Carangidae).[2] De wetenschappelijke naam van de soort is voor het eerst geldig gepubliceerd in 1801 door Lacepède.
Bronnen, noten en/of referentiesCampogramma glaycos é uma espécie de peixe pertencente à família Carangidae.
A autoridade científica da espécie é Lacepède, tendo sido descrita no ano de 1801.
Encontra-se presente em Portugal, onde é uma espécie nativa.
Os seus nomes comuns são enxareu-palheta, xareu-palheta, xareu-palmeta.
Trata-se de uma espécie marinha. Atinge os 60 cm de comprimento à furca nos indivíduos do sexo masculino.
Campogramma glaycos é uma espécie de peixe pertencente à família Carangidae.
A autoridade científica da espécie é Lacepède, tendo sido descrita no ano de 1801.
Vadigo (Campogramma glaycos) är en fisk i familjen taggmakrillfiskar som förekommer i östra Atlantens varmare delar.
Vadigon har en oval och från sidorna sammantryckt kropp[2] med grågrön rygg, silverfärgad undersida och en följd av flikar i ryggens respektive undersidans färger på sidorna. Stjärtfenan är kraftigt urgröpt. Den har två ryggfenor, av vilka den främre endast består av en serie taggar. Unga fiskar har dessa taggar förenade av en tunn hinna, som senare försvinner.[3] Den blir upp till 60 cm lång, och kan som mest väga 2,8 kg.[4]
Arten är en aktiv, snabbsimmande fisk[2] som lever pelagiskt eller strax ovan bottnen på ett djup mellan 15 och 30 m. Födan består främst av stimfiskar, men även ryggradslösa bottendjur kan ingå i dieten[2]. Äggen är pelagiska.[4]
Vadigon finns i östra Atlanten från Brittiska öarna över Madeira, västra Medelhavet och Kanarieöarna till Senegal.[4]
Ett visst trålfiske förekommer.[4] Arten är dessutom en populär sportfisk.[2]
Vadigo (Campogramma glaycos) är en fisk i familjen taggmakrillfiskar som förekommer i östra Atlantens varmare delar.
大齒鰺(学名:Campogramma glaycos),为輻鰭魚綱鱸形目鱸亞目鰺科的一个种,分布於東大西洋,從不列顛群島至加納利群島海域,包括地中海西部,為亞熱帶海水魚,棲息深度15-30公尺,體長可達60公分,成魚棲息在大洋或淺海區,以其他魚類為食,生活習性不明,可做為食用魚及遊釣魚。
大齒鰺(学名:Campogramma glaycos),为輻鰭魚綱鱸形目鱸亞目鰺科的一个种,分布於東大西洋,從不列顛群島至加納利群島海域,包括地中海西部,為亞熱帶海水魚,棲息深度15-30公尺,體長可達60公分,成魚棲息在大洋或淺海區,以其他魚類為食,生活習性不明,可做為食用魚及遊釣魚。