zh-CN
导览中的名字

El Rhizopus és un gènere de floridura que inclou espècies cosmopolites de fongs zigomicets filamentosos que es troben al sòl, degradant els fruits i vegetals, excrements animals i residus.
Rhizopus ist eine Gattung der Schimmelpilze in der Ordnung der Mucorales. Einige Arten werden vor allem in Fernost zur Fermentation von Lebensmitteln verwendet, andere sind gefürchtete Pflanzenpathogene.
Rhizopus-Kulturen bilden einen spinnwebenartigen Pilzrasen mit flachen Ausläufern. An den Stellen, an denen Rhizoidhyphen im Substrat verankert sind, stehen die dicht büscheligen, unverzweigten, bräunlichen und bis 3 Millimeter langen Sporangienträger.
Die Sporangien sind weißlich bis schwarz und rundlich mit einem Durchmesser zwischen 150 und 350 Mikrometer. Die Columella ist rundlich und verjüngt sich mit deutlicher Apophyse zu den Trägern hin.
Die Sporen sind mehr oder weniger oval, zwischen 10 und 15 Mikrometer lang sowie 6 bis 8,5 Mikrometer breit.
Rhizopus-Arten finden sich auf faulenden Pflanzenteilen und im Erdboden. Die Sporen sind in der Luft häufig und verbreiten sich schnell. Insbesondere Rhizopus nigricans befällt häufig Lebensmittel.
In Deutschland sind nur vier Arten verbreitet, dafür aber sehr häufig. In den Tropen finden sich viele andere Arten.
Die Gattung Rhizopus steht in der Ordnung der Mucorales, dort wurde sie in die Familie der Mucoraceae gestellt. Eng verwandte Gattungen sind Absidia, Apophysomyces, Mucor und Rhizomucor.
Nach morphologischen Gesichtspunkten lässt sich die Gattung in drei Gruppen einteilen, eine molekularbiologische Untersuchung aus dem Jahr 2006 bestätigte diese drei Gruppen im Wesentlichen. Dies sind:
Die Position von vielen anderen Arten, wie Rhizopus schipperae, Rhizopus nigricans und anderen, ist noch umstritten.
Rhizopus ist eine Gattung der Schimmelpilze in der Ordnung der Mucorales. Einige Arten werden vor allem in Fernost zur Fermentation von Lebensmitteln verwendet, andere sind gefürchtete Pflanzenpathogene.
Rhizopus is a genus of common saprophytic fungi on plants and specialized parasites on animals. They are found in a wide variety of organic substances, including "mature fruits and vegetables",[2] jellies, syrups, leather, bread, peanuts, and tobacco. They are multicellular. Some Rhizopus species are opportunistic human pathogens that often cause fatal disease called mucormycosis. This widespread genus includes at least eight species.[3][4]
Rhizopus species grow as filamentous, branching hyphae that generally lack cross-walls (i.e., they are coenocytic). They reproduce by forming asexual and sexual spores. In asexual reproduction, sporangiospores are produced inside a spherical structure, the sporangium. Sporangia are supported by a large apophysate columella atop a long stalk, the sporangiophore. Sporangiophores arise among distinctive, root-like rhizoids. In sexual reproduction, a dark zygospore is produced at the point where two compatible mycelia fuse. Upon germination, a zygospore produces colonies that are genetically different from either parent.
Various species, including R. stolonifer, may cause soft rot in sweet potatoes and Narcissus.
Rhizopus helps in nutrient development since this species is grown in soil it ferments the fruits and vegetable in the soil inhibiting the growth and develops certain pathogens that inhibits the growth of toxigenic fungus.[5] In addition to that, there is even a type of Rhizopus (Rhizopus microsporus-fermented soybean tempe) that has proven to reduce colon carcinogenesis in rats by elevating factors of mucins, immunoglobulin A, and organic acids and give protection to piglets from Escherichia coli-infection by inhibiting adhesion to the intestinal membranes. [6]
Phylogeny
Rhizopus is a genus of common saprophytic fungi on plants and specialized parasites on animals. They are found in a wide variety of organic substances, including "mature fruits and vegetables", jellies, syrups, leather, bread, peanuts, and tobacco. They are multicellular. Some Rhizopus species are opportunistic human pathogens that often cause fatal disease called mucormycosis. This widespread genus includes at least eight species.
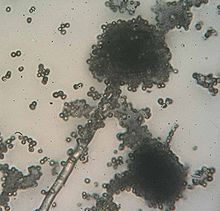 Rhizopus 400x magnification
Rhizopus 400x magnification Rhizopus species grow as filamentous, branching hyphae that generally lack cross-walls (i.e., they are coenocytic). They reproduce by forming asexual and sexual spores. In asexual reproduction, sporangiospores are produced inside a spherical structure, the sporangium. Sporangia are supported by a large apophysate columella atop a long stalk, the sporangiophore. Sporangiophores arise among distinctive, root-like rhizoids. In sexual reproduction, a dark zygospore is produced at the point where two compatible mycelia fuse. Upon germination, a zygospore produces colonies that are genetically different from either parent.
Rhizopus oligosporus is used to make tempeh, a fermented food derived from soybeans. Rhizopus oryzae is used in the production of alcoholic beverages in parts of Asia and Africa. Rhizopus stolonifer (black bread mold) causes fruit rot on strawberry, tomato, and sweet potato and used in commercial production of fumaric acid and cortisone.Various species, including R. stolonifer, may cause soft rot in sweet potatoes and Narcissus.
Rhizopus helps in nutrient development since this species is grown in soil it ferments the fruits and vegetable in the soil inhibiting the growth and develops certain pathogens that inhibits the growth of toxigenic fungus. In addition to that, there is even a type of Rhizopus (Rhizopus microsporus-fermented soybean tempe) that has proven to reduce colon carcinogenesis in rats by elevating factors of mucins, immunoglobulin A, and organic acids and give protection to piglets from Escherichia coli-infection by inhibiting adhesion to the intestinal membranes.
Phylogeny
The mating analysis has also been found which was comparative that this species structure is flexible in comparison with other species in the same genus. The topology length of the species genome is found to be three times bigger with the species.Rhizopus estas genro de fungo. Ili estas saprofitaj kaj kelkfoje iomete parazita de frukto aŭ de legomoj. Oni uzas Rhizopus por fabriki tempeon.
Rhizopus es un género de mohos que incluyen especies cosmopolitas de hongos filamentosos hallados en el suelo, degradando frutos y vegetales, heces animales, y residuos.
Las especies de Rhizopus producen esporas asexuales y sexuales. Las esporangiosporas asexuales se producen dentro de una estructura aguzada, el esporangium, y son genéticamente idénticas a su padre. En Rhizopus, el esporangio es soportado por una gran columela apofisada, y el esporangióforo asoma entre rizpodes distintivos. Zigosporas negras se producen después de dos fusiones compatibles de micelios durante la reproducción sexual. Y hacen colonias que pueden ser genéticamente diferentes de sus padres.
Algunas spp. de Rizopus son agentes oportunistas de zigomicosis humana. Pueden causar serias (y con frecuencia mortales) infecciones en humanos y en animales debido a su rápido crecimiento a relativamente altas temperaturas. Algunas especies son patógenos vegetales. Dos son usados en fermentación: Rhizopus oligosporus, en la producción de tempeh, un alimento fermentado derivado de grano de soja; R. oryzae se usa en la producción de bebidas alcohólicas, en partes de Asia y de África. Hongo filamentoso que presenta esporangióforos sin ramificar (de hasta 2 mm x 20 µm), de color pardo oscuro que nacen de un gran nudo de rizoides bien desarrollados. Esporangios esféricos negros (de hasta 275 µm de diámetro) con columela. Esporangiosporas negras de 8 a 15 µm. Abundantes rizoides y zigosporas esféricas de pared gruesa, desnuda (de hasta 200 µm de diámetro). Clamidosporas ausentes. Colonias de crecimiento rápido (cubren prácticamente toda la superficie de la placa en tres días a 25 °C) de aspecto consistente, con denso micelio aéreo, algodonosas, al principio blancas, después gris oscuras (micelio rojizo, grisáceo o marrón) (Figura 72). Se reconoce fácilmente por sus espolones hialinos o parduzcos, sus rizoides numerosos y pardos y sus esporangios negros y lustrosos (brillantes).
Rhizopus es un género de mohos que incluyen especies cosmopolitas de hongos filamentosos hallados en el suelo, degradando frutos y vegetales, heces animales, y residuos.
Las especies de Rhizopus producen esporas asexuales y sexuales. Las esporangiosporas asexuales se producen dentro de una estructura aguzada, el esporangium, y son genéticamente idénticas a su padre. En Rhizopus, el esporangio es soportado por una gran columela apofisada, y el esporangióforo asoma entre rizpodes distintivos. Zigosporas negras se producen después de dos fusiones compatibles de micelios durante la reproducción sexual. Y hacen colonias que pueden ser genéticamente diferentes de sus padres.
Algunas spp. de Rizopus son agentes oportunistas de zigomicosis humana. Pueden causar serias (y con frecuencia mortales) infecciones en humanos y en animales debido a su rápido crecimiento a relativamente altas temperaturas. Algunas especies son patógenos vegetales. Dos son usados en fermentación: Rhizopus oligosporus, en la producción de tempeh, un alimento fermentado derivado de grano de soja; R. oryzae se usa en la producción de bebidas alcohólicas, en partes de Asia y de África. Hongo filamentoso que presenta esporangióforos sin ramificar (de hasta 2 mm x 20 µm), de color pardo oscuro que nacen de un gran nudo de rizoides bien desarrollados. Esporangios esféricos negros (de hasta 275 µm de diámetro) con columela. Esporangiosporas negras de 8 a 15 µm. Abundantes rizoides y zigosporas esféricas de pared gruesa, desnuda (de hasta 200 µm de diámetro). Clamidosporas ausentes. Colonias de crecimiento rápido (cubren prácticamente toda la superficie de la placa en tres días a 25 °C) de aspecto consistente, con denso micelio aéreo, algodonosas, al principio blancas, después gris oscuras (micelio rojizo, grisáceo o marrón) (Figura 72). Se reconoce fácilmente por sus espolones hialinos o parduzcos, sus rizoides numerosos y pardos y sus esporangios negros y lustrosos (brillantes).
Rhizopus Zygomycota taldean sailkatzen den onddo mota bat da. Onddoak, orokorrean, hiru talde nagusitan sailka daitezke, morfologiari dagokionez: legamiak (onddo zelulabakarrak), lizunak (hifa izeneko filamentuak dituztenak) eta perretxikoak (gorputz fruitu-emaile handiak dituztenak, kapela itxurakoak, askotan jan egiten direnak). Rhizopus onddoa lizunen taldean sailkatzen da, hifa luzeak baititu.
Onddo hauek habitat desberdinetan bizi dira: lurzoruan, hondatzen ari diren ogi, fruta eta landareetan, animalien gorotzetan, etab.
Era asexualean eta sexualean ugaltzen dira, bi ugalketa mota horiek txandakatuz. Era asexualean endosporak sortzen dituzte, esporangio izeneko egituretan. Era sexualean onddoaren bi hifa ezberdinak elkartzen dira, zigospora izeneko esporak sortuz. Zigosporak heltzen direnean espora asexualak ekoizten dituzte, airearen bidez barraiatzen direnak onddo mizelio berriak eratuz.
Rhizopus-en esporangioak ilunak izan ohi dira. Columela izeneko egitura baten muturrean daude, substratuari finkatzen dena errizoideen bidez (ikus irudia).
Rhizopus nigricans ogiaren lizuna da, ogi hezean agertu ohi dena elikagai hori hondatzen denean. Onddo hori erabilera industriala du kortisonaren ekoizpenean. Onddoak erreakzio kimiko espezifikoa burutzen du, kortisonaren aitzindari baten hidroxilazioa, hain zuzen ere. Aldaketa kimiko horri bioeraldaketa deritzo, mikroorganismo batek eragiten duelako. Bioeraldaketa horri esker, prozesu industrialetan kortisona molekula erraz lortzen da, botika gisa erabiltzen dena hantura prozesuei aurre egiteko.
Rhizopus batzuk landareen patogenoak dira, eta beste batzuk giza patogenoak. Azken hauek zigomikosi izeneko gaitza eragiten dute, batez ere immunitate-sistema ahulduta duten pertsonengan.
Rhizopus Zygomycota taldean sailkatzen den onddo mota bat da. Onddoak, orokorrean, hiru talde nagusitan sailka daitezke, morfologiari dagokionez: legamiak (onddo zelulabakarrak), lizunak (hifa izeneko filamentuak dituztenak) eta perretxikoak (gorputz fruitu-emaile handiak dituztenak, kapela itxurakoak, askotan jan egiten direnak). Rhizopus onddoa lizunen taldean sailkatzen da, hifa luzeak baititu.
Onddo hauek habitat desberdinetan bizi dira: lurzoruan, hondatzen ari diren ogi, fruta eta landareetan, animalien gorotzetan, etab.
Era asexualean eta sexualean ugaltzen dira, bi ugalketa mota horiek txandakatuz. Era asexualean endosporak sortzen dituzte, esporangio izeneko egituretan. Era sexualean onddoaren bi hifa ezberdinak elkartzen dira, zigospora izeneko esporak sortuz. Zigosporak heltzen direnean espora asexualak ekoizten dituzte, airearen bidez barraiatzen direnak onddo mizelio berriak eratuz.
Rhizopus-en esporangioak ilunak izan ohi dira. Columela izeneko egitura baten muturrean daude, substratuari finkatzen dena errizoideen bidez (ikus irudia).
Rhizopus nigricans ogiaren lizuna da, ogi hezean agertu ohi dena elikagai hori hondatzen denean. Onddo hori erabilera industriala du kortisonaren ekoizpenean. Onddoak erreakzio kimiko espezifikoa burutzen du, kortisonaren aitzindari baten hidroxilazioa, hain zuzen ere. Aldaketa kimiko horri bioeraldaketa deritzo, mikroorganismo batek eragiten duelako. Bioeraldaketa horri esker, prozesu industrialetan kortisona molekula erraz lortzen da, botika gisa erabiltzen dena hantura prozesuei aurre egiteko.
Rhizopus batzuk landareen patogenoak dira, eta beste batzuk giza patogenoak. Azken hauek zigomikosi izeneko gaitza eragiten dute, batez ere immunitate-sistema ahulduta duten pertsonengan.
(RLQ=window.RLQ||[]).push(function(){mw.log.warn("Gadget "ErrefAurrebista" was not loaded. Please migrate it to use ResourceLoader. See u003Chttps://eu.wikipedia.org/wiki/Berezi:Gadgetaku003E.");});Rhizopus est un genre de moisissures communes qui se développent sous forme de filaments dans les sols, sur les fruits et les végétaux en décomposition, sur les fèces des animaux et sur le pain. Il fait partie de l'ordre des Mucorales.
Il produit à la fois des spores sexuées et des spores asexuées.
Les Rhizopus comme les autres mucorales étaient rattachés aux Zygomycota mais cette ancienne division considérée comme artificielle car polyphylétique n'est plus retenue par les systématiciens depuis 2007 et la publication par un large groupe de travail d'une synthèse sur la classification phylogénétique au niveau des rangs élevés chez les champignons[1]. Dans la classification de niveau plus fin les Rhizopus étaient situés parmi les mucoracées. Cette vaste famille très hétérogène a vu beaucoup de ses membres reclassés. Aussi depuis 2012[2] Hoffmann et al. proposent la création de la famille des Rhizopodaceae[3],[4].
La morphologie de l'anamorphe se caractérise par une hyphe siphonnée (sans cloison), multinucléée, à noyaux haploïdes, et à croissance apicale, possédant une paroi de chitine et de glucanes.
Le protoplasme renferme de nombreuses vacuoles qui repoussent le cytoplasme et les noyaux à la périphérie. Les réserves de nourriture sont stockées sous forme de glycogène et de lipides.
Au moment de la reproduction, ou après une blessure, des septa (cloisons) sont formées.
Le genre Rhizopus se caractérise parmi les autres genres de l'ordre des Mucorales[5] par :
.
Le mycélium est lâche, extensif, cotonneux devenant brun-noir à maturité. Lorsqu'il envahit le substrat, il se manifeste comme une moisissure duveteuse, blanchâtre puis grise. À la loupe, on distingue clairement les fructifications noirâtres (sporocystophore et sporocystes).
(l'espèce type)
Certaines espèces de Rhizopus peuvent être responsables de mucormycose, une infection qui peut être fatale pour l'homme ou l'animal.
Des cultures de Rhizopus peuvent être utilisées en production alimentaire.
Rhizopus est un genre de moisissures communes qui se développent sous forme de filaments dans les sols, sur les fruits et les végétaux en décomposition, sur les fèces des animaux et sur le pain. Il fait partie de l'ordre des Mucorales.
Il produit à la fois des spores sexuées et des spores asexuées.
Rhizopus adalah genus fungi saprofit yang umum pada tanaman dan parasit yang terspesialisasi pada hewan. Mereka ditemukan di berbagai substrat organik, termasuk "buah dan sayuran matang",[2] jeli, sirup, kulit, roti, kacang tanah, dan tembakau. Beberapa spesies Rhizopus adalah agen oportunistik dari zigomikosis manusia (infeksi jamur) dan bisa berakibat fatal. Infeksi Rhizopus juga bisa menjadi komplikasi ketoasidosis diabetik.[3] Genus yang tersebar luas ini mencakup setidaknya delapan spesies.[4][5]
Spesies Rhizopus tumbuh sebagai hifa berbentuk filamen dan bercabang yang umumnya tidak memiliki dinding silang (yaitu koenositik). Mereka berkembang biak dengan membentuk spora aseksual dan seksual. Dalam reproduksi aseksual, sporangiospora diproduksi di dalam struktur berbentuk bola, yaitu sporangium. Sporangium didukung oleh kolumela apophysate besar di atas tangkai yang panjang, sporangiofor. Sporangiofor muncul di antara rizoid khas yang mirip akar. Dalam reproduksi seksual, zigospora gelap diproduksi pada titik di mana dua miselium yang kompatibel melebur. Setelah berkecambah, zigospora menghasilkan koloni yang secara genetis berbeda dari induk-induknya.
Berbagai jenis, termasuk R. stolonifer, dapat menyebabkan busuk lunak pada ubi jalar dan narsis.
Rhizopus adalah genus fungi saprofit yang umum pada tanaman dan parasit yang terspesialisasi pada hewan. Mereka ditemukan di berbagai substrat organik, termasuk "buah dan sayuran matang", jeli, sirup, kulit, roti, kacang tanah, dan tembakau. Beberapa spesies Rhizopus adalah agen oportunistik dari zigomikosis manusia (infeksi jamur) dan bisa berakibat fatal. Infeksi Rhizopus juga bisa menjadi komplikasi ketoasidosis diabetik. Genus yang tersebar luas ini mencakup setidaknya delapan spesies.
Spesies Rhizopus tumbuh sebagai hifa berbentuk filamen dan bercabang yang umumnya tidak memiliki dinding silang (yaitu koenositik). Mereka berkembang biak dengan membentuk spora aseksual dan seksual. Dalam reproduksi aseksual, sporangiospora diproduksi di dalam struktur berbentuk bola, yaitu sporangium. Sporangium didukung oleh kolumela apophysate besar di atas tangkai yang panjang, sporangiofor. Sporangiofor muncul di antara rizoid khas yang mirip akar. Dalam reproduksi seksual, zigospora gelap diproduksi pada titik di mana dua miselium yang kompatibel melebur. Setelah berkecambah, zigospora menghasilkan koloni yang secara genetis berbeda dari induk-induknya.
R. microsporus var. oligosporus digunakan untuk membuat tempe, makanan fermentasi yang berasal dari kedelai. R. oryzae digunakan dalam produksi minuman beralkohol di beberapa wilayah Asia dan Afrika. Rhizopus stolonifer (kapang roti hitam) menyebabkan buah membusuk pada stroberi, tomat, dan ubi jalar dan digunakan dalam produksi komersial asam fumarat dan kortison.Berbagai jenis, termasuk R. stolonifer, dapat menyebabkan busuk lunak pada ubi jalar dan narsis.
Il Rhizopus è un genere di muffe che si trova generalmente nel suolo, nella frutta e nella verdura marce, nelle feci animali e nel pane andato a male.
Le diverse specie di Rhizopus producono spore per via sia sessuale che asessuale. Le sporangiospore asessuali sono prodotte dentro una struttura simile a una capocchia di spillo, lo sporangio, e sono geneticamente identiche al loro genitore. Le zigospore sono prodotte dopo la fusione di due miceli durante la riproduzione sessuata e danno vita a colonie geneticamente diverse dai loro genitori.
Alcune specie di Rhizopus possono colpire l'uomo, provocando forme di zigomicosi analoghe a quelle prodotte dal genere Mucor. Le zigomicosi animali e umane dovute a queste specie costituiscono infezioni serie e anche fatali a causa del rapido ritmo di crescita.
Altre specie sono patogene per le piante, come Rhizopus nigricans e Rhizopus arrhizus. Due specie sono invece utili. Rhizopus oligosporus è usato per la produzione del tempeh, pane di soia fermentata popolare in Indonesia. Rhizopus oryzae invece è usato per la produzione di bevande alcoliche in Asia.
Il Rhizopus è un genere di muffe che si trova generalmente nel suolo, nella frutta e nella verdura marce, nelle feci animali e nel pane andato a male.
Rhizopus is een wijdverspreid geslacht van saprofyte schimmels die als parasieten op planten en dieren worden aangetroffen. Ze komen voor op rijpe groenten en fruit[1], feces, zoete voedingsmiddelen als jam en stroop, leer, brood, pinda's en tabak. Sommige soorten kunnen ook optreden als opportunistische infecties bij mensen en kunnen dodelijk zijn. Deze infecties kunnen een complicatie zijn van ketoacidose bij diabetespatiënten.[2]
Schimmels van het geslacht Rhizopus zijn draadachtig van vorm. De schimmeldraden zijn vertakt en hebben geen tussenwanden tussen de cellen. De sporangia zijn duidelijk te herkennen op de top van de sporangioforen.
Het geslacht Rhizopus bevat tien soorten:[3]
Rhizopus is een wijdverspreid geslacht van saprofyte schimmels die als parasieten op planten en dieren worden aangetroffen. Ze komen voor op rijpe groenten en fruit, feces, zoete voedingsmiddelen als jam en stroop, leer, brood, pinda's en tabak. Sommige soorten kunnen ook optreden als opportunistische infecties bij mensen en kunnen dodelijk zijn. Deze infecties kunnen een complicatie zijn van ketoacidose bij diabetespatiënten.
Schimmels van het geslacht Rhizopus zijn draadachtig van vorm. De schimmeldraden zijn vertakt en hebben geen tussenwanden tussen de cellen. De sporangia zijn duidelijk te herkennen op de top van de sporangioforen.
Rhizopus Ehrenb. – rodzaj grzybów z gromady sprzężniaków (Zygomycota)[1].
Są to grzyby mikroskopijne tworzące watowate, kosmate plechy z zarodniami. Początkowo plechy mają barwę od białej do żółtawej, wkrótce jednak od zarodników ciemnieją i stają się szare do brązowych Charakterystyczną cechą tego rodzaju jest wytwarzanie stolonów i pigmentowanych chwytników oraz wyrastanie sporangioforów bezpośrednio nad chwytnikami. Po uwolnieniu się zarodników kolumelle często zwijają się, tworząc strukturę podobną do parasola (tzw. apofizę)[2] . Przy rozróżnianiu gatunków odgrywają rolę takie cechy morfologiczne, jak: długość strzępek, kształt i długość sporangioforów i kolumelli, średnica zarodni oraz wielkość, kształt i powierzchnia zarodników, a nawet cechy fizjologiczne, takie np., jak maksymalna temperatura wzrostu[3].
Występuje zarówno rozmnażanie płciowe, jak i bezpłciowe. Rozmnażanie płciowe zachodzi na drodze zygogamii (jest to rodzaj gametangiogamii). Rhizopus jest heterotaliczny, to znaczy, że wytwarza dwa rodzaje strzępek, które morfologicznie zupełnie nie różnią się od siebie, są jednak zróżnicowane płciowo, co oznacza się jako (+) i (-). Gdy zetkną się dwie odmienne płciowo strzępki (+) i (-), najpierw następuje oddzielenie poprzeczną ścianą końcowego odcinki strzępki (zygoforu). Powstaje w ten sposób wielojądrowe gametangium. Ściany dwóch stykających się z sobą gametangiów rozpuszczają się i ich zawartość zlewa się, co nazywa się plazmogamią. W jądrach komórkowych pochodzących od obydwu gametangiów następują podziały mitotyczne. Teraz następuje zlewanie się jąder pochodzących od różnych gametangiów, czyli wielokrotna kariogamia. Powstaje wielojądrowa zygospora o diploidalnej liczbie chromosomów. Otacza się ona grubą ściana o ciemnej barwie i przechodzi w okres spoczynku trwający kilka miesięcy. W tym okresie pełni więc funkcję przetrwalnika. Gdy zaczyna kiełkować, zaraz w jej jądrach zachodzi mejoza i powstają jądra haploidalne[4].
Z kiełkujących zygospor rozwijają się strzępki powietrzne z chwytnikami, oraz sporangiofory z zarodniami. W zarodniach na drodze bezpłciowej wytwarzane są zarodniki (sporangiospory). Roznosi je wiatr, ale prawdopodobnie także woda, owady i niektóre inne drobne zwierzęta[5].
Rhizopodaceae, Mucorales, Incertae sedis, Incertae sedis, Mucoromycotina, Zygomycota, Fungi[1].
Należy do monotypowej rodziny Rhizopodaceae K. Schum. 1894[6].
Crinofer Nieuwl., Mucor P. Micheli ex Fr., Mucor subgen. Rhizopus (Ehrenb.) J. Schröt., Pilophora Wallr., Zygambella Nagal. & Subrahm[7]:
Nazwy naukowe na podstawie Index Fungorum[8].
Gatunki należące do rodzaju Rhizopus to zarówno saprotrofy odżywiające się martwą materią organiczną, jak i pasożyty wywołujące choroby roślin, zwierząt i ludzi. Gatunki saprotroficzne pojawiają się często na żywności powodując pleśnienie owoców i nasion. Niektóre gatunki mają znaczenie medyczne, powodują bowiem zakażenia skórne (grzybice)[3].
Rhizopus Ehrenb. – rodzaj grzybów z gromady sprzężniaków (Zygomycota).
Rhizopus é um "sapróbio comum e parasita facultativo de frutos e vegetais maduros".[1] É um género de bolores que inclui fungos filamentosos cosmopolitas encontrados no solo, frutos e vegetais em decomposição, fezes de animais e pão velho.
As espécies de Rhizopus produzem esporos sexuais e assexuais. Os esporangiósporos assexuais são produzidos no interior de uma estrutura com forma de cabeça de alfinete, o esporângio, e são geneticamente idênticos ao seu progenitor. Os esporângios são suportados por uma grande columela apofisada, e os esporangióforos surgem entre rizoides distintos. Zigósporos escuros são produzidos após a fusão de dois micélios compatíveis durante a reprodução sexuada. Dão origem a colónias que podem ser geneticamente diferentes dos seus progenitores.
Algumas espécies de Rhizopus são agentes infecciosos oportunistas da zigomicose humana. Podem causar infeccções sérias (e muitas vezes fatais) em humanos e animais devido à sua elevada taxa de crescimento e por poderem desenvolver-se a temperaturas relativamente elevadas. Algumas espécies são patógenos vegetais. Duas são utilizadas na fermentação de alimentos: Rhizopus oligosporus, é usada na produção de tempeh, um alimento fermentado derivado de grãos de soja, e de oncom; R. oryzae é usado na produção de bebidas alcoólicas em partes da Ásia e África.
As infecções por Rhizopus são uma complicação associada à cetoacidose diabética.[2]
|day= ignorado (|data=) sugerido (ajuda) Rhizopus é um "sapróbio comum e parasita facultativo de frutos e vegetais maduros". É um género de bolores que inclui fungos filamentosos cosmopolitas encontrados no solo, frutos e vegetais em decomposição, fezes de animais e pão velho.
As espécies de Rhizopus produzem esporos sexuais e assexuais. Os esporangiósporos assexuais são produzidos no interior de uma estrutura com forma de cabeça de alfinete, o esporângio, e são geneticamente idênticos ao seu progenitor. Os esporângios são suportados por uma grande columela apofisada, e os esporangióforos surgem entre rizoides distintos. Zigósporos escuros são produzidos após a fusão de dois micélios compatíveis durante a reprodução sexuada. Dão origem a colónias que podem ser geneticamente diferentes dos seus progenitores.
Algumas espécies de Rhizopus são agentes infecciosos oportunistas da zigomicose humana. Podem causar infeccções sérias (e muitas vezes fatais) em humanos e animais devido à sua elevada taxa de crescimento e por poderem desenvolver-se a temperaturas relativamente elevadas. Algumas espécies são patógenos vegetais. Duas são utilizadas na fermentação de alimentos: Rhizopus oligosporus, é usada na produção de tempeh, um alimento fermentado derivado de grãos de soja, e de oncom; R. oryzae é usado na produção de bebidas alcoólicas em partes da Ásia e África.
As infecções por Rhizopus são uma complicação associada à cetoacidose diabética.
Ризопус (чорна цвіль) частіше всього з'являється на фруктах та овочах при їх довгому зберіганні. Пошкоджує поверхню плоду, а також його нутрощі (м'якуш фруктів забарвлюється в коричневий колір, починається процес бродіння). Представники цього роду належать до типу зигомікотів (до нижчих грибів — фікомікотів). Зигомікотові гриби включають гриби родів Mucor, Rhizopus, Absidia, Rhizomucor, Basidiobolus, Conidiobolus. Широко поширені в грунті, повітрі, їжі, на гниючих рослинах, плодах. Більшість видів Rhizopus є сапротрофами (редуценти) і харчуються різною мертвою органічною речовиною, хоча деякі види є паразитами або патогенними. Розвиток міцелію при низьких температурах помітно сповільнюється, а спорангії перетворюються в щільну масу — чорну або темно-сіру.[2]
Гриби роду Rhizopus характеризуються розгалуженним міцелієм, що складаються з трьох типів гіфів: столони (дугоподібно вигнуті гіфи), ризоїдів, якими прикліплюється до субстрату і зазвичай негалуджених спорангієносців. На кінцях спорангієносців знаходяться округлені, чорні спорангії. У спорангіях утворюються численні нерухомі багатоядерні спорангіоспори для безстатевого розмноження. Rhizopus може розмножуватися і статевим шляхом, коли присутні два сумісних і фізіологічно різних міцеліїв. При статевому процесі утворюють зигоспори. Швидко зростаючі колонії змінюють свій колір від білого до темного.[3]
Rhizopus cohnii псує сіно і солому та інші корми, особливо якщо вони були заскиртовані вологими. «Заважає» нормальному збереженню врожаїв зернових, спричиняючи їх гниття. Тим же чином провокує втрати серед закладених на зберігання груш, бульб картоплі, кореневищ ірису, коренеплодів буряка цукрового, яблук та інших «м'ясистих» плодів.
Rhizopus microsporus викликає буру суху гниль кошиків соняшнику.
Rhizopus necans вражає цибулини лілій м'якою гниллю. При зберіганні їх в досить теплих умовах вони гинуть через 45-50 годин.
Rhizopus nigricans з'являєтья на фруктах дерев з родів груша і яблуня, а також на персиках. Продукує Кагатну гниль цукрових буряків, мокру гниль на бульбах батату, чорну цвіль на насінні пшениці і на хлібобулочних виробах, якщо вони неправильно зберігаються. Псує м'якою гниллю картоплю, проникаючи в бульби крізь ходи, погризені личинками жуків-коваликів (так званими проволочниками). Проникнувши в ягоди винограду крізь травмовану шкірку, розм'якшує, руйнує їх плоть і обумовлює дострокове закінчення соку. Згубний для зібраних ягід ожини, суниці, полуниці, малини. Для баклажана є менш шкідливий, хоча може «прикрашати» цвіллю — знову ж чорної — його плоди і в відкритому грунті, в теплицях.
Rhizopus nodosus викликає сіру гниль кошиків соняшнику, коренеплодів буряків, культурних різновидів бавовнику, на гронах різних сортів винограду, на солодких фігах інжиру.
Rhizopus oryzae схожий на Rhizopus cohnii, проте приносить ще й користь. В азійських країнах давно виявлено, що у Rhizopus oryzae висока ферментативна активність, і тому застосовують його як один з інгредієнтів закваски для сировини, з якого бажають отримати спиртовмісний напій. Крім того, він поряд з Rhizopus japonicus і Rhizopus oligosporus, допомагає зброджувати рослинне молоко, що готується з насіння сої харчової, перетворюючи його в «темпі» або в «тофу» («соєвий сир»). Аналогічну процедуру можна зробити не тільки з бобами сої, але і з ядрами плодів кокосової пальми, і з зернами рослин з родини злакових — зокрема, рису.[1]
Rhizopus oligosporus викристовується для ферментезації сої та виготовлення темпе.[4]
Багато представників роду Rhizopus мають високу ферментативну активність або утворюють різні органічні кислоти, завдяки чому знаходять практичне застосування, особливо в країнах Азіатського континенту. Ці гриби використовуються як компонент закваски («китайські дріжджі», «раги») або безпосередньо для ферментативного виробництва зброджених продуктів харчування («соєвий сир», «темпі» та інші). З бобів сої, зерна злаків (рису та інших), ядра кокосового горіха, а також для отримання спирту з бульб картоплі. Деякі гриби роду Rhizopus викликають зигомікоз (фікомікоз) у імунодефіцитних осіб (інвазивний легеневий зигомікоз, ураження шлунково-кишкового тракту, шкіри, мозку та інших органів). Спори грибів проникають в організм аерогенним (повітряно-капельним) шляхом або при контакті з травмованими тканинами (аліментарним шляхом) і шкіри (контактним шляхом). Поширюючись в природі, призводять до загибелі врожаю і викликають захворювання у рослин.[2]
1. У місцях зберігання врожаю рекомендується забезпечувати посилену примусову циркуляцію повітря. До концентрації в ньому кисню O2 Ризопуси не вимогливі, проте часті провітрювання сприяють зниженню стовпчика термометра, що дуже бажано. Діапазон температур, при яких може розвиватися, наприклад, Rhizopus nigricans, досить широкий — 5-45 ° C, але взагалі цього паразита (як і його «братів» по роду) вважають теплолюбним, бо з'ясовано, що найкраща для нього температура лежить в межах 30-35 °С.
2. Висока відносна вологість повітря теж більш комфортна для розвитку Ризопусів, ніж низька. Значить, якщо дощова погода затягується, то шанси зіткнутися в саду, на полі або в городі з «буйством» цих грибків збільшуються.
3. Своєчасно очищати субстрат від будь-яких бур'янів і залишків рослин, на яких можуть міститися (а то і зимувати) спори Ризопусів.
4. Щоб пригальмувати поширення хвороби від однієї ягоди до іншої, щільні грона столових сортів винограду в періоди зростання і визрівання прийнято проріджувати. Для винних сортів аналогічну процедуру вважають економічно виправданою, замість неї грона звільняють від ягід пошкоджених, явно заражених або просто підозрілих, обкурюють сірчистим газом (двоокис сірки SO2, спрацьовує як консервант) і без затримок охолоджують.
5. Плодові дерева за 12-14 днів до зняття врожаю треба обприскувати фунгіцидами.
6. Дезінфекція тари, яка планується використовуватися для збору плодів та овочів, а також стіни, полиці і інші конструкційні елементи всередині сховища.
7. Знищення шкідників, які допомагають рознесенню зарази.
8. Для своєчасного виявлення ступеня зараженості сховищ пліснявими грибами необхідно проводити регулярний мікробіологічний контроль.[5]
根黴屬(学名:Rhizopus)真菌主要外觀特徵為具有假根(rhizoid)及匍匐菌絲(stolon)。孢子囊柄(sporangiophore)以單支或數支成束的方式自匍匐菌絲長出,孢子囊柄基部往往與假根基部相對。孢子囊柄不分枝,其頂端有一圓球形孢子囊(sporangium),囊內有許多孢囊孢子(sporangiospore)。孢子囊有囊軸、囊領、囊托等構造,成熟時呈現灰色至褐色。
孢囊孢子呈圓球形、橢球形或不規則球形,表面有紋路。產生孢囊孢子為根黴屬真菌的無性繁殖方式之一。另一種根黴屬真菌的無性繁殖方式為菌絲局部膨大形成厚膜孢子(chlamydospore)。
根黴屬真菌的有性繁殖方式為產生接合孢子(zygospore)。不同交配型的氣生菌絲形成的配子囊彼此接觸後產生接合孢子,配子囊表面無紋路,接合孢子表面則有突起物。
根黴屬真菌中的少孢根霉(Rhizopus oligosporus)為製作丹貝的主要菌種。
根黴屬(学名:Rhizopus)真菌主要外觀特徵為具有假根(rhizoid)及匍匐菌絲(stolon)。孢子囊柄(sporangiophore)以單支或數支成束的方式自匍匐菌絲長出,孢子囊柄基部往往與假根基部相對。孢子囊柄不分枝,其頂端有一圓球形孢子囊(sporangium),囊內有許多孢囊孢子(sporangiospore)。孢子囊有囊軸、囊領、囊托等構造,成熟時呈現灰色至褐色。
孢囊孢子呈圓球形、橢球形或不規則球形,表面有紋路。產生孢囊孢子為根黴屬真菌的無性繁殖方式之一。另一種根黴屬真菌的無性繁殖方式為菌絲局部膨大形成厚膜孢子(chlamydospore)。
根黴屬真菌的有性繁殖方式為產生接合孢子(zygospore)。不同交配型的氣生菌絲形成的配子囊彼此接觸後產生接合孢子,配子囊表面無紋路,接合孢子表面則有突起物。
 分類(目以上はHibbett et al. 2007) 界 : 菌界 Fungi 門 : incertae sedis 亜門 : ケカビ亜門 Mucoromycotina 目 : ケカビ目 Mucorales 科 : クモノスカビ科 rhizopodaceae 属 : クモノスカビ属 Rhizopus 種
分類(目以上はHibbett et al. 2007) 界 : 菌界 Fungi 門 : incertae sedis 亜門 : ケカビ亜門 Mucoromycotina 目 : ケカビ目 Mucorales 科 : クモノスカビ科 rhizopodaceae 属 : クモノスカビ属 Rhizopus 種 本文参照
クモノスカビ(Rhizopus)は、菌界・接合菌門・接合菌綱・ケカビ目・クモノスカビ科(あるいはケカビ科)に属するカビの和名である。基質表面をはう菌糸の様子がクモの巣を思わせることから、その名がある。
クモノスカビは、湿った有機物表面に出現する、ごく普通のカビである。空中雑菌として出現することも多い。
体制はケカビに似ている。菌糸体は多核体の菌糸からなり、基質中に菌糸をのばすが、基質表面から気中へと匍匐菌糸をのばすのが特徴である。匍匐菌糸は基質の上をはい、基質につくとそこから菌糸をのばす。そのため、ケカビに比べると、コロニーの成長が早く、あっというまに広がる。基質の表面に広がる気中菌糸は、その表面に水滴がつき、きらきらと輝き、クモの巣のように見える。
無性生殖は、胞子のう胞子による。胞子嚢柄は匍匐菌糸が基質に付着したところから出て、その下には仮根状菌糸が伸びる。胞子のう柄はほとんど分枝せず、先端に大きな胞子のうを1つつける。胞子のうは、ケカビのものによく似ているが、胞子のう柄の先端がすこし広がって胞子のうに続き、胞子のう内部の柱軸になめらかに続いている(ケカビでは、胞子のう柄は胞子のうのところでくびれる)。このような胞子のう直下のふくらみをアポフィシスと呼び、ケカビ目の属の分類では重要な特徴とされる。ただし、ユミケカビ(Absidia)ほど明瞭ではないので、見分けにくい場合もある。
胞子は、胞子嚢の壁が溶けることで放出される。はじめは壁がとろけてできた液粒の中に胞子が入った状態だが、すぐに乾燥し、柱軸も乾いて傘状に反り返り、その表面に胞子が乗った状態になる。クモノスカビの胞子はケカビなどにくらべて乾燥に強そうな、丈夫な表面を持ち、条模様が見られるのが普通である。
有性生殖は、ケカビと同じように、配偶子のう接合によって接合胞子のうを形成する。一部の種をのぞいては自家不和合性なので、接合胞子のうを見掛けることは少ない。接合胞子のう柄はH字型で、丸くふくらむ。接合胞子のうは黒褐色に着色し、その表面は凹凸がある。
クモノスカビは、基本的には腐生であるが、弱い寄生菌として、植物の病原体になる場合がある。食物の上に出現することも多い。モモなどの柔らかい果実について、その腐敗を早めることもある。
極めて成長が早いので、微生物の培養時にコンタミとしてこれが侵入すると、一夜にして全てを覆いつくす。胞子もよく飛ぶのでいやがられる。
他方、コウジカビを使う日本以外のアジア全域において、紹興酒などの酒の醸造で麹[1]に用いられたり、インドネシアでは茹でた大豆に生やしてテンペ(Tempeh)という食品にする例がある。
古くからよく知られた属であり、ケカビ目を代表するものの一つでもある。古典的な分類体系では大型の胞子嚢のみを形成し、接合胞子嚢の様子もケカビに近いものであるため、ケカビ科に含めた。また、アポフィシスを持つことからケカビ科を細分してユミケカビ科としたこともある。ただし、このような形態に基づく分類体系は、分子系統によって示された系統関係とかけ離れたものであることが示され、見直しが進みつつある。Hoffmann et al.(2013)ではこの属をスポロディニエラ、フタマタケカビ Syzygites と共にクモノスカビ科としており、この研究結果で認められた群の中では比較的よくまとまった群をなしているとしている。
100を越える種が記載されている。形態が単純で分類が難しい類でもある。実際の種数は十数種といわれる。